- Home
- Search
- Images
- Species Checklists
- US States: O-Z >
- US National Parks
- Central America
- South America
- US National Parks
- Southern Subpolar Region
|
|
|
|
Family: Lecideaceae
[Biatora berengeriana A. Massal., moreBiatora berengeriana var. berengeriana A. Massal., Biatora berengeriana var. lecanodes (Nyl.) Walt. Watson, Biatora cupreiformis (Nyl.) Arnold, Lecidea berengeriana var. berengeriana (A. Massal.) Nyl., Lecidea berengeriana var. lecanodes (Nyl.) A.L. Sm., Lecidea berengeriana var. perileuciza Nyl. ex Cromb., Lecidea cuprea subsp. berengeriana (A. Massal.) Cromb., Lecidea cuprea var. cupreiformis Nyl., Lecidea cupreiformis (Nyl.) Nyl., Lecidea cupreiformis var. cupreiformis (Nyl.) Nyl., Lecidea cupreiformis var. lecanodes Nyl., Mycobilimbia berengeriana (A. Massal.) Hafellner & V. Wirth] |
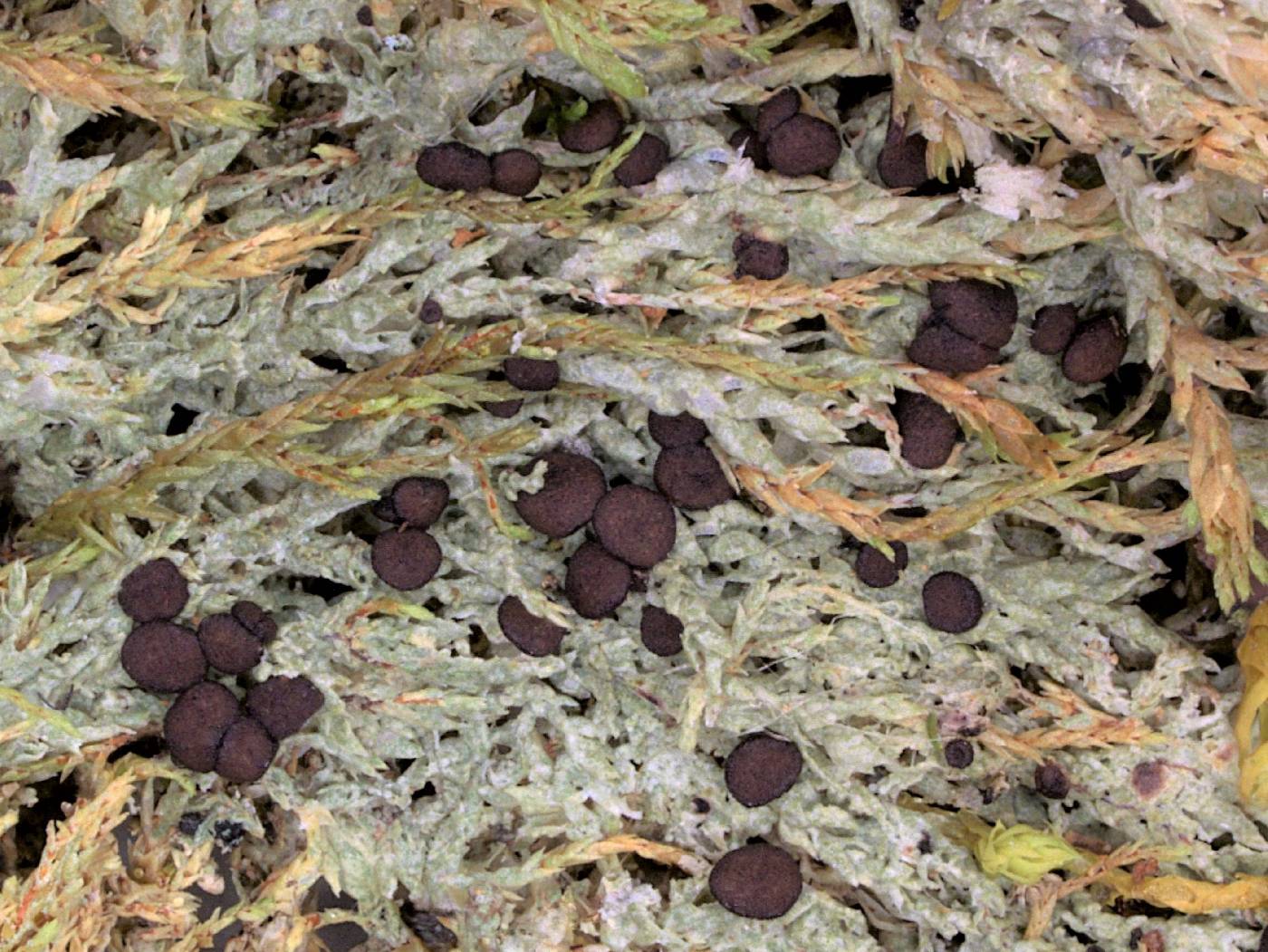
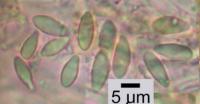
Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bungartz, F., (eds.) 2004. Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 2. Thallus: composed of minute warts areoles: irregular in outline, moderately to strongly convex, sometimes marginally incised, 0.05-0.3 mm in diam. surface: greenish gray to pale ochre, dull, esorediate cortex: poorly developed, hyaline, 5-10 µm thick medulla: mostly lacking; algal layer: 70-100 µm thick Apothecia: rounded to somewhat deformed, sessile with a constricted base, 0.35-0.8(-1.1) mm wide disc: reddish brown to brown-black, initially concave, soon plane or weakly convex margin: same color as disc or paler outside, persistent or excluded in older apothecia exciple: brown in upper parts or near hymenium, usually lighter brown or almost hyaline below, laterally 50-80 µm, basally 95-250 µm wide, composed of radiating hyphae with 1-4.5 µm to apically 2-6.5 µm wide lumina epihymenium: orange brown or red-brown, 5-15 µm high, often poorly delimited against hymenium hymenium: hyaline, sometimes with pale brown stripes, rarely with blackish blue granules of "hypnorum-blue", 55-75 µm tall; paraphyses: hyaline or pale brown at the apices, below 1-2 (-3) µm wide to apically 1.5-4.5(-6.5) µm wide lumina, weakly branched and anastomosing subhymenium: often darker than hypothecium, rarely with blackish blue granules of "hypnorum-blue" (Meyer and Printzen 2000) hypothecium: brown; hypothecium and subhymenium: together 175-270 µm thick asci: clavate, ±Porpidia-type, with a I+ blue tholus containing a distinct darker blue tube structure in the center, 8-spored ascospores: hyaline, simple, fusiform-ellipsoid, (8.5-)10.4-14.8(-16.5) x (3.8 )4.4-5(-5.5) µm; walls: often with a rough perispore 0.5 µm wide Pycnidia: not seen. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC-, P- Secondary metabolites: none detected by TLC. Substrate and ecology: on bryophytes over rock and soil between c. 600 and 3350 m World distribution: circumpolar in boreal regions of the Northern Hemisphere Sonoran distribution: Arizona and southern California. Notes: In Sonoran specimens the thallus is rather thin and brittle compared with European material. So far Lecidea berengeriana is the only muscicolous/ terricolous Sonoran species of Lecidea s. lat. Mycobilimbia carneoalbida and M. tetramera can be similar in outward appearance, but are distinguished by having 3-septate spores, narrower paraphyses and excipular hyphae and a paler hypothecium. Mycobilimbia olivacea has a similar ascus type and spores, but it grows on wood and bark and is readily distinguished by its dark green, subsquamulose thallus, ±emarginate apothecia, and its hyaline hypothecium. Global occurrence: Eurasia – Asia Extratropical | Eurasia – Europe | Americas – North America (incl Mexico) | Eurasia – Asia Tropical | Arctic. Substrate: soil, clay, humus, turf, detritus, dead leaves | bryophytes – mosses, liverworts. Life habit: lichenized (mutualistic with algal photobionts). Thallus: crustose (crustaceous) – episubstratal – unspecified; continuous, diffuse, effuse | granular, granulose, granulate; [th] upper surface: white(ish) | green(ish) grey | white(ish) grey; [th upper surface]: epruinose; [th marginal and upper surface] specific structures: absent; [th] morphol substructures (eg areoles, lobes, branches) width [mm]: (min) 0.04 (low) 0.1 (high) 0.3 (max) 0.5; [th] morphol substructures (eg areoles, squamules): contiguous, coherent (throughout the thallus); [th] morphol substructures (eg areoles, lobes, branches) upper surface: granulose, granular | verrucose, warted. Ascomata: absent | present; ascoma: apothecial, apothecioid – hymenial; ascoma [mm]: (low) 0.3 (high) 0.9 (max) 1.5; [ascm, if apoth] disc, mazaedium: plane, flat, flattened, expanded | subconvex, slightly convex | convex | strongly convex, hemispherical, (sub-)globose; [ascm, if apoth] disc, mazaedium: black(ish) | brown(ish) (if pale: fawn, tan; if mid: cinnamon) | black(ish) brown; [ascm, if apoth] margin surface; [if perith] periostiolar area, ostiole, involucrellum: red(dish) brown (if pale: orange brown); [ascm, if apoth] subhymenial layers, hypothecium; [if perith] basal excipulum: red(dish) brown (if pale: orange brown); [ascm] paraphyses/-oids: present; [ascm] paraphyses/-oid cells width [µm]: (low) 1.5 (high) 2.0 (max) 2.5; [ascm] paraphyses/-oid apical cells width [µm]: (low) 4.0 (high) 5.0 (max) 6.0; [ascm] epihymenium, epithecium: yellow(ish) brown. Asci: lecanoralean; [asc] tholus: thickened; [asc] tholus amyloidity (iodine reaction): present; [asc] tholus amyloidity pattern: with amyloid tube, ring (= Collema-, Micarea-, Porpidia-, Psora-types etc). Ascospores: (median) 8.0; [asp] shape: elongate-fusiform, ellipsoidal-fusiform; [asp] length [µm]: (min) 9.0 (low) 11.0 (high) 16.0 (max) 19.0; [asp] width [µm]: (low) 4.0 (high) 5.0 (max) 6.0; [asp] septa: absent – spore lumen unilocular, monolocular; [asp] pigmentation: hyaline, colourless; [asp] perispore, epispore: ornamented, rough, warted, striate, cracked. Secondary metabolites: absent. Primary photobiont: present, chlorophytaceous – trebouxiaceous, chlorococcoid. Secondary photobionts (eg in cephalodia): absent. |
|
|
|