Consortium of Lichen Herbaria
- building a Global Consortium of Bryophytes and Lichens as keystones of cryptobiotic communities -
- Home
- Search
- Images
- Species Checklists
- US States: O-Z >
- US National Parks
- Central America
- South America
- US National Parks
- Southern Subpolar Region
|
|
|
|
Family: Caliciaceae
|
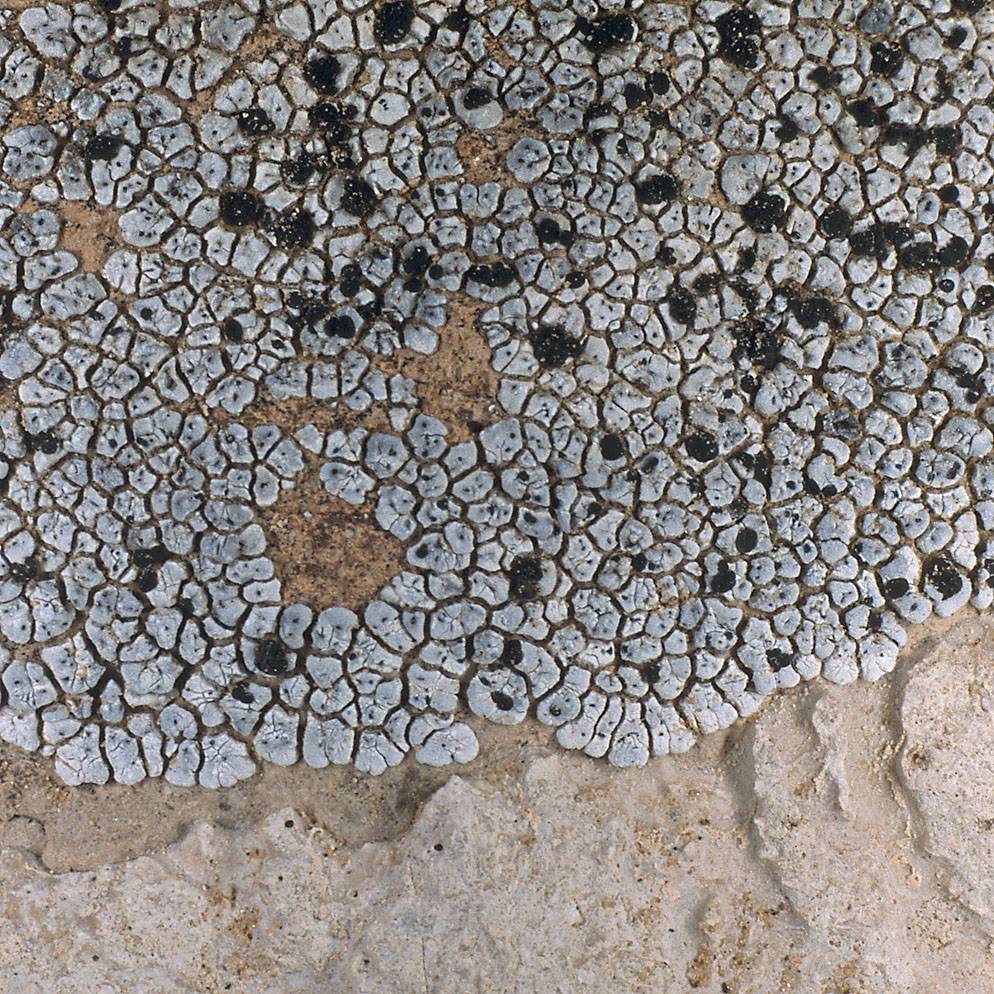
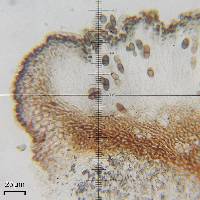
Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bungartz, F., (eds.) 2007. Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 3. Thallus: crustose, areolate to subsquamulose, thick, ±continuous or becoming dispersed; prothallus: absent surface: usually ivory, beige to deep brown or gray, rarely lead gray, dull or ±shiny, smooth to deeply fissured, with fine or coarse pruina, rarely epruinose, phenocorticate, esorediate medulla: white, with few, rarely large amounts of calcium oxalate (H2SO4+ needle shaped crystals) Apothecia: lecideine; (0.4-)0.6-1.1(-1.2) mm in diam., sessile margin: black, thin to thick, usually persistent, rarely excluded with age disc: black, usually epruinose or rarely with white pruina, plane, often becoming strongly convex with age proper exciple: dispersa-type, inner excipular hyphae distinct, not reduced, pigmented, prosoplectenchymatous (textura oblita), extending from the deep reddish brown hypothecium (leptoclinoides-brown, textura intricata), outer excipular hyphae short-celled, cells angular, distinctly swollen (textura angularis) and carbonized with various amounts of a brown pigment (cf. elachista-brown) and only small amounts of a diffuse aeruginose pigment (cinereorufa-green, HNO3+ violet, restricted to the outermost exciple cells) epihymenium: only the outermost exciple cells aeruginose, pigmentation not continuous with the exciple (HNO3- !!!) hymenium: hyaline, not inspersed with oil droplets; paraphyses: simple to moderately branched, apically swollen, with a brown pigment cap (cf. elachista-brown, aeruginose pigment not extending across epihymenium) asci: clavate, Bacidia-type, 8-spored ascospores: soon brown, 1-septate, oblong to ellipsoid, usually not constricted, with obtuse ends, not curved, (11-) 12.9-[14.5]-16.1(-19) x (6-)6.5-[7.3]-8.1(-9) µm (n=60); proper septum: becoming soon but only briefly thickened during spore ontogeny (±Physconia-type); ornamentation: microrugulate Pycnidia: rare, urceolate to globose, unilocular; ontogeny similar to the Umbilicaria-type conidiogenous cells: mostly terminal, rarely also intercalary (cf. conidiophore-type V) conidia: bacilliform, 5-10 x 1.5-2 µm (n=20) Spot tests: K+ yellow to red (sometimes weak, usually forming crystals), P+ yellow (sometimes weak), C-, KC-, CK- fluorescence: UV- (pale) iodine reaction: medulla non-amyloid Secondary metabolites: atranorin, norstictic, connorstictic, and ±stictic acids (J. A. Elix, HPLC). Substrate and ecology: epilithic, on a variety of siliceous (HCl-) rock substrates, rarely also on sandstones with small amounts of carbonates (HCl+) World and Sonoran distribution: common throughout Arizona, southern California, Baja California, Baja California Sur, and Chihuahua. Notes: Buellia nashii closely resembles B. dispersa, but contains norstictic acid and has an aeruginose, HNO3+ violet outer exciple. Buellia nashii was described from the Sonoran Region, where it is common although absent from lower desert elevations. It also extends into adjacent areas. |
Powered by Symbiota