Consortium of Lichen Herbaria
- building a Global Consortium of Bryophytes and Lichens as keystones of cryptobiotic communities -
- Home
- Search
- Images
- Species Checklists
- US States: O-Z >
- US National Parks
- Central America
- South America
- US National Parks
- Southern Subpolar Region
|
|
|
|
Family: Lichinaceae
|
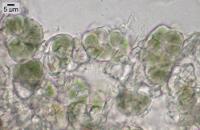
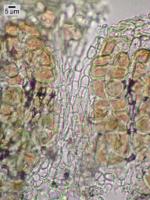
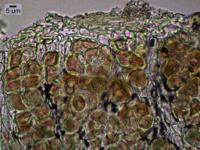
Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bungartz, F., (eds.) 2002. Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 1. Thallus: peltate, irregularly orbicular or oval in outline, lobate lobes: up to 8 mm in diam., frequently deeply concave; margins: incurved or raised and easily broken upper surface: grayish pruinose or rarely brownish when without pruina; margin: rough, sometimes appearing granular or almost sorediate upper cortex: pseudoparenchymatous, 8-50 µm thick, cells 5-12 µm wide; epinecral layer: 20-50 µm thick medulla: with anticlinally arranged hyphae, 3.5-8 µm thick, at the base with enlarged globose cells (up to 12 µm in diam.); cyanobacteria distributed throughout lower cortex: not developed Apothecia: one to several per lobe; disc: red-brown, at first deeply urceolate and subsequently becoming shallowly concave, up to 1.5 mm diam.; exciple: 45-60 µm thick; hymenium: 115-160 µm tall, I+ blue, in part reddish; subhymenium: 28-60 µm asci: cylindrical to obovoid, 8-spored ascospores: simple, ellipsoid to fusiform, 18-20 x 8-13 µm Pycnidia: immersed conidia: fusiform, 2.5-3.5 x 1-1.5 µm Spot tests: all negative Secondary metabolites: none detected. Substrate and ecology: usually on soil, sometimes on soil over acidic rocks, occasionally in calcareous areas World distribution: SW and intermountain areas of western North America Sonoran distribution: desert areas of Arizona, California, and Baja California. Notes: The species is often collected sterile, but its gray, deeply concave thallus and rough margin are sufficiently distinctive that it can be readily recognized. Most other Heppiae and Peltulae are olive or brownish-olive colored. |
|
|
|
Powered by Symbiota